Introduction to Arrays
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array). The base value is index 0 and the difference between the two indexes is the offset.
For simplicity, we can think of an array as a fleet of stairs where on each step is placed a value (let’s say one of your friends). Here, you can identify the location of any of your friends by simply knowing the count of the step they are on.
Content:
- Concept of array
- Properties of array
- Advantage of C array
- Disadvantage of C array
- Types of arrays in c
- One dimensional arrays in c
- Two dimensional arrays in c
- Multi dimensional arrays in c
- Declaration and initialization of array
- Compile time initialization
- Run time initialization
- Application of arrays
Concept of array:
- Definition : Array is a fixed-size sequenced collection of elements of the same data type. (Derived data type)
- An array is a derived data type.
- Array is useful concept for representing a group of similar value under a single name.
- Array can be defined simply as the group of same data type.
- Whenever a particular value from a group is needed, we can access it by name of array and the position of the value in the group.
- An array is used to represent a list of numbers , or a list of names.
- Example:-
- List of employees in an organization
- Test scores of a class of students.
- List of customers and their telephone numbers
- List of students in the college.
- For Example, to represent 100 students in college , can be written as student [100]
- Position is called a index or superscript. Base index = 0.
- It allocates sequential memory locations.
- Individual values are called as elements.
Properties of Array:
The array contains the following properties.
- Each element of an array is of same data type and carries the same size, i.e., int = 4 bytes.
- Elements of the array are stored at contiguous memory locations where the first
- element is stored at the smallest memory location.Elements of the array can be randomly accessed since we can calculate the address of each element of the array with the given base address and the size of the data element.
Advantage of C Array:
1) Code Optimization: Less code to the access the data.
2) Ease of traversing: By using the for loop, we can retrieve the elements of an array easily.
3) Ease of sorting: To sort the elements of the array, we need a few lines of code only.
4) Random Access: We can access any element randomly using the array.
Disadvantage of C Array:
1) Fixed Size: Whatever size, we define at the time of declaration of the array, we can't exceed the limit. So, it doesn't grow the size dynamically like Linked List which we will learn later.
Access Array Elements:
You can access elements of an array by indices.
Suppose you declared an array mark as above. The first element is mark[0], the second element is mark[1] and so on.
Few keynotes:
- Arrays have 0 as the first index, not 1. In this example, mark[0] is the first element.
- If the size of an array is n, to access the last element, the n-1 index is used. In this example, mark[4]
- Suppose the starting address of mark[0] is 2120d. Then, the address of the mark[1] will be 2124d. Similarly, the address of mark[2] will be 2128d and so on.
This is because the size of a float is 4 bytes
Types of arrays :
Types of Arrays: We can use arrays to represent not only simple lists of values but also tables of data in two or three or more dimensions.
- One – dimensional arrays
- Two – dimensional arrays
- Multi dimensional arrays
1.One Dimensional array:
- A variable which represent the list of items using only one index (subscript) is called one-dimensional array.
- For Example, if we want to represent a set of five numbers say(35,40,20,57,19), by an array variable number, then number is declared as follows
- int number [5] ;
- Computer store these numbers as shown below:
- number [0]
- number [1]
- number [2]
- number [3]
- number [4]
- The values can be assigned to the array as follows
- number [0] = 35;
- number [1] = 40;
- number [2] = 20;
- number [3] = 57;
- number [4] = 19;
Exercise:
- we want to represent a set of five students cpu subject marks say (80,90,50,57,64), by an array variable cpu_marks.
- Solution:
- The values can be assigned to the array as follows
- Solution:
- The values can be assigned to the array as follows
How to declare an array?
For example:
float mark[5];
Here, we declared an array, mark, of floating-point type. And its size is 5. Meaning, it can hold 5 floating-point values.
It's important to note that the size and type of an array cannot be changed once it is declared
Declaration of One Dimensional array:
- Syntax :
- Here the type specifies the data type of elements contained in the array, such as int, float, or char.
- And the size indicates the maximum numbers of elements that can be stored inside the array.
- The size should be either a numeric constant or a symbolic constant.
- For example :
- Here int is type, group is a variable name , 10 is a size of array and the subscripts (index) is start from 0 to 9.
- Declares the height to be an array containing 50 real elements. Any index 0 to 49 are valid
- Declares the group as an array to contain a maximum of 10 integer numbers.
- Declares the name as a character array (string) variable that can hold a maximum of 10 characters.
- Valid Statement of array:
number[4] = number[0] + number[2];
number[2] = x[5] + y[10];
value[6] = number[i] * 3;
Initialization of One Dimensional array:
An array can be stored in following stages :
- At compile time
- At run time
1. Compile time initialization :
• In compile time initialization, the array is initialized when they are declared.
• The general form of initialization of array is :
type array-name[size] = { list of values };
• The list of values are separated by commas.
Example :
int number[3] = {4,5,9};
• Here array number of size 3 and will assign 4 to first element(number[0]), 5 is assign with second element(number[1]) and 9 is assign with third element(number[2]).
• In compile time initialization, the array is initialized when they are declared.
• The general form of initialization of array is :
type array-name[size] = { list of values };
• The list of values are separated by commas.
• If the number of values in the list is less than the number of elements, then only that many elements will be initialized. The remaining elements will be set to zero automatically.
Example :
int number[ ] = {1,2,3,4};
• The character array can be initialized as follows :
char name[ ] = {‘j’,’o’,’h’,’n’,’\0’};
• The character array can also be initialized as follows :
char name[ ] = “john”;
2. Run time initialization :
• In run time initialization, the array is explicitly initialize at run time.
• This concept generally used for initializing large arrays.
Example:
for(i=0; i < 100; i++)
{
if( i < 50) sum[i] = 0.0;
else sum[i] = 1.0;
}
• Here first 50 elements of the array sum are initialized to 0 and the remaining 50 elements are initialized to 1 at run time.
Write a program using a single dimensional array to read and display the array elements.
main( )
{
int i, x[10];
printf(“Enter 10 numbers: \n”);
for (i=0; i <10; i++)
{
scanf(“ %d ”, &x[i]);
}
printf(“The array elements are:”);
for(i=0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf(“%d \t”, x[i]);
}
getch( );
}
Output:
Enter 10 numbers:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
The array elements are:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
- We can also use a read function such as ‘scanf’ to initialize an array.
int x[3];
scanf(“ %d %d %d ”, &x[0], &x[1], &x[2]);
OR
int x[3];
for(i=0; i<2; i++)
{
scanf(“ %d ”, &x[i]);
}
- Write a program to find out the largest and smallest element in an array.
main( )
{
int i,n,a[50], large, small;
printf(“Enter size of array:”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
printf(“\n Array elements are \n”);
for(i=0; i
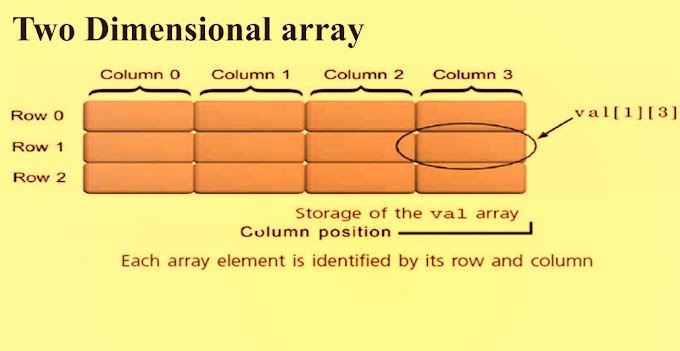
Two Dimensional array :
A list of items can be given one variable name using two subscripts and such a variable is called a two – subscripted variable or a two –dimensional array.
Two dimensional are used to represent the two dimensional structures like matrix, table etc. The two-dimensional array is declared as follows Datatype
Where row_size denotes total number of rows and column size denotes total number of column.
Initialization of Two Dimensional array:
- This initializes the elements of first row to zero and the second row to one.
- Initialization is done row by row. 🙠 The above statement can be equivalently written as
- we can also initialize a two – dimensional array in the form of a matrix as shown below:
- Commas are required after each brace that closes of a row, except in case of last row.
- When all the elements are to be initialized to zero, the following short-cut method may be used.
- The following statement will also achieve the same result
- The memory layout of above example :
C Array Example: Sorting an array:
In the following program, we are using bubble sort method to sort the array in ascending order.
#include<stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int i, j,temp;
int a[10] = { 10, 9, 7, 101, 23, 44, 12, 78, 34, 23};
for(i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
for(j = i+1; j<10; j++)
{
if(a[j] > a[i])
{
temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
printf("Printing Sorted Element List ...\n");
for(i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
printf("%d\n",a[i]);
}
}
Program to print the largest and second largest element of the array.
#include<stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int arr[100],i,n,largest,sec_largest;
printf("Enter the size of the array?");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the elements of the array?");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
largest = arr[0];
sec_largest = arr[1];
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(arr[i]>largest)
{
sec_largest = largest;
largest = arr[i];
}
else if (arr[i]>sec_largest && arr[i]!=largest)
{
sec_largest=arr[i];
}
}
printf("largest = %d, second largest = %d",largest,sec_largest);
}
- Write a program to display the elements of two dimensional array.
- OUTPUT:
Multi Dimensional array:
- A variable which represent the list of items using more than two index (subscript) is called multi-dimensional array.
- The general form of multi dimensional array is :
- Where S is the size. Some examples are :
- Here survey is a three-dimensional array and it contain 90 (3*5*6) integer type elements. And table is a four-dimensional array and it contain 300 floating type elements.
Application Of Arrays:
- Using pointers for accessing arrays.
- Passing arrays as function parameters.
- Arrays as members of structures.
- Using structure type data as array element.
- Arrays as dynamic data stuctures.
- Manipulating character arrays and strings.










0 Comments